Top Hardware-Software Integration Trends You Must Know in 2025

With each passing day, technological breakthroughs are reshaping the modern computing world. While hardware and software have always been distinct by nature, integrating the two unlocks incredible potential, thereby delivering powerful and adaptable systems that fulfill modern users requirements.
From powering devices through AI applications to exploring next-level computing efficiency, over 80% of businesses now believe that hardware-software integration is at the core of today’s tech revolution. It’s driving innovation and helping businesses tackle real-world challenges with smarter and more efficient solutions.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at the key hardware-software integration trends of 2025 that any forward-thinking enterprises can’t afford to ignore.
Why Hardware Needs Software Integration
Hardware consists of physical components designed for specific tasks, but when integrated with custom software or applications, its functionalities expand significantly. This kind of integration is known as hardware software integration that allows the software to communicate with and control devices in real-time, creating a cohesive ecosystem where every component operates in sync.
With automation and integration solutions requirements rising rapidly, the system integration market is projected to reach $872.23 billion by 2032 with a CAGR of 10.5% between 2025 and 2032. This surge reflects a clear trend: the increasing reliance on software-defined hardware solutions to streamline processes, expedite data analysis, improve communication, and unlock data-driven decision-making.
After all, software is what brings life to even the most advanced hardware, enabling them to:
Perform specific tasks automatically
Process and analyze real-time data
Control hardware devices with precision
Communicate with other systems seamlessly
Generate insights for smarter decision-making
Think about your smartphone. On the outside, it’s a sleek, compact device, but inside, it’s packed with powerful hardware like processors, cameras, and sensors. Without software, none of it would function the way we expect. It’s software that makes everything work together seamlessly, from recognizing your fingerprint or face ID to processing data in real-time.
The same applies to smart home devices. A simple tap on your phone lets you adjust the temperature or turn off the lights in your home. No need to be in the room or even at home. With smart home apps, you can control everything remotely, making life a whole lot easier.
In healthcare, hardware-software integration is transforming patient care by improving connectivity between medical devices and biomedical applications. Real-time monitoring of vital signs, instant access to patient data, and AI-powered diagnostics are leading to faster medical interventions and better patient outcomes. With these systems in place, healthcare professionals can rely on real-time data to make informed decisions and provide better treatment.
One of the biggest advantages of hardware-software integration is flexibility. Developers can continuously roll out new features or enhancements through software updates, without needing to modify or replace the underlying hardware.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the latest hardware-software integration trends that every business needs to know.
Key Trends in Hardware/Software Integration
With businesses relying more on software solutions and custom applications to manage everything from operations to customer interactions, the demand for integrated systems is skyrocketing.
Companies are no longer looking at hardware and software as separate entities, but as interconnected components that work together to boost efficiency, improve decision-making, and enhance user experience. The rise of AI, IoT, and cloud computing has pushed businesses to adopt smarter, software-driven hardware that can adapt, learn, and respond in real-time.
As this transformation gains momentum, here’s a look at the top trends driving hardware-software integration:
Real-time Data Integration is Powering the Future of Connected Tech
In today’s fast-paced digital environment, businesses are increasingly dependent on system integration to connect hardware and software in a way that actually delivers value. With data pouring in from IoT sensors, industrial machines, smart devices, and more, companies need reliable systems that can handle real-time data processing, execute operations instantly, and automate complex tasks efficiently.

A big reason this is becoming more achievable is due to the rise of SaaS companies that are building specialized applications, many now powered by AI to tackle a wide range of business challenges. That said, with the flood of apps entering the market, it’s hard to predict how many will actually stand the test of time or survive the competition.
The Advantages:
For businesses, this capability enables timely decision-making, drastic elimination of data silos, and minimal latency across operations. This means that teams across departments can access accurate, real-time information, which improves coordination and productivity. For end users, it results in better customer experiences, like being able to conveniently handle and interact with the hardware or receive instant alerts when something goes wrong.
The Challenges:
Real-time integration isn’t always smooth sailing. Delays in data processing and challenges in managing large volumes of incoming data can slow things down. These issues often stem from outdated infrastructure, limited bandwidth, or insufficient system resources that just can’t keep up with the data demands of today’s connected environments.
AI/ML Will Simplify Integrations
Today, the way artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning (ML) algorithms are transforming businesses is wild. These technologies are not only streamlining interactions and enabling parallel processing but are also automating routine development tasks, all while driving down costs with minimal human intervention. At this pace, it’s difficult to predict where AI will take us next because right now, it’s the driving force behind much of the innovation we’re seeing in hardware-software integration.
Thanks to forward-thinking software development companies that are riding this wave, building smarter ways to integrate AI into applications to improve device performances, personalize user experiences, and improve overall system efficiency. For example, Goose is Google’s in-house AI, trained on decades of engineering know-how. Employees use it to write code faster and build products more efficiently.
AI hardware is at the heart of the AI revolution, empowering businesses to extract insights, automate processes, and deliver new levels of efficiency and customer experiences.
– Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai
The Advantages:
With software development becoming increasingly complex and product feature demands growing rapidly, AI is proving to be a game-changer. It supports hardware engineers and software developers across the entire lifecycle, from design and prototyping to testing and deployment by significantly cutting down manual efforts and error-prone processes.
AI is also playing a pivotal role in software-hardware co-development. It helps design adaptable hardware that can be programmed easily for optimal performance through specialized software. For instance, AI can analyze usage data from smart home devices to automatically suggest software optimizations, or process patient vital signs from smart medical devices to fine-tune configurations in real-time.
Additionally, AI/ML models are now capable of conducting extensive virtual assessments far more efficiently than traditional manual testing, thereby accelerating time to market without compromising quality.
The Challenges:
Now, while all this sounds amazing, AI integration also brings a fair share of challenges.
First off, you need a lot of data to properly train and validate AI models. And not just any data, you need high-quality, diverse, and accurate datasets. That’s not always easy to source, especially for niche or emerging use cases.
Second, there’s still a big gap in collaboration between hardware engineers and software developers. AI-driven systems need hardware that’s flexible enough to roll with frequent software updates, and getting everyone aligned on that can be a challenge.
And finally, hardware software integration complexity is a real thing. As AI systems get smarter, the backend gets messier. Compatibility issues, infrastructure limitations, and syncing everything in real time, that’s where things can start to break down if the foundation isn’t solid.
Low-Code Development Will Level Up Hardware Software Integrations
Support for low-code platforms is more than just a passing trend and it’s here to stay. As companies race to build smarter and more efficient solutions, low-code tools are quickly becoming essential for boosting productivity and accelerating development cycles.
With intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces, visual workflows, and libraries of pre-built components, platforms like OutSystems, Hostinger, Mendix, Superblocks, and Microsoft Power Apps are making it possible for both experienced developers and non-coders to build applications that support hardware integration without starting from scratch every time.
Some platforms claim to cut app development time by up to 90%, while using over 70% fewer resources than traditional methods. No surprise then, that by 2030, the low-code market is expected to soar beyond $187 billion.
The Advantages:
One of the biggest perks of low-code integrations is rapid prototyping. Businesses can now test ideas quickly, spin up department-specific tools, or respond to user feedback without waiting on long dev cycles. It’s great for teams who need to move fast and want working software in days, not months.
And, even experienced developers are using low code to skip the boring parts. Instead of spending time building out the same login screen or admin dashboard for the hundredth time, they use low-code platforms to get the basics in place and focus on the stuff that actually moves the needle, like integrating with hardware devices or optimizing performance.
Another huge plus is the cross-platform support. Most low-code platforms let you build once and deploy across web, mobile, and sometimes even embedded systems. So, if you’re developing an app that interfaces with a piece of industrial hardware or a wearable device, you don’t have to rewrite it three different times. It’s all centralized, clean, and efficient.
The Challenges:
That said, low-code isn’t the holy grail. There are some underlying challenges to note.
Scalability is the biggest one. Low-code apps can struggle when hardware requirements evolve, or when the need for advanced customization arises. For example, if you’re integrating with real-time robotics hardware or building firmware-specific interfaces, you’ll quickly outgrow low code’s capabilities. That’s when native or high-code integration becomes non-negotiable.
Security is another concern. While platforms like Zoho Creator or Bubble may offer built-in security features, apps built by non-technical users can overlook basics like proper data handling, input validations, secure API usage, or version control. That leaves room for vulnerabilities, even in seemingly simple applications.
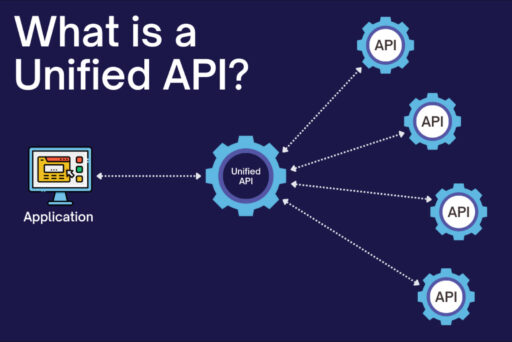
Unified APIs Are Making Hardware-Software Integrations So Much Easier
Unified APIs are turning into a serious game-changer for hardware software integrations. As connected devices keep multiplying across industries, the need for seamless integration has become non-negotiable.
With unified APIs, you don’t have to write separate code for every device or platform, you get one consistent interface that connects everything. They offer a single, standardized way to connect and interact with multiple hardware platforms or third-party services, without having to build every integration from scratch.
The Advantages:
Unified APIs follow a one-time authentication model, so once you’re authenticated, you can access connected platforms and devices without logging in or verifying credentials every time. This means no juggling tokens or dealing with extra steps.
Real-time syncing is another advantage. Unified APIs automatically fetch and update data across connected systems, which means no more delays or stale dashboards. This is especially useful in industries like transportation or healthcare, where timely data literally drives decisions.
Then there’s simplified troubleshooting with solid documentation. Since all data and requests flow through a central API system, it’s easier to track issues, monitor performance, and fix bugs quickly. And because most unified API platforms come with proper documentation and pre-built connectors, developers don’t have to waste hours reverse-engineering bad or inconsistent documents.
The Challenges:
Here are some of the limitations of unified APIs that are important to consider.
Compatibility issues between systems are a serious concern in hardware integrations. Not all proprietary hardware or legacy platforms are designed to support unified APIs. In industries with long product life cycles, like manufacturing or healthcare, some devices may still rely on proprietary protocols or outdated APIs. This often forces developers to build custom bridges, defeating the whole purpose of using a unified solution.
Another issue is functionality. While unified APIs are great for standard use cases, they can fall short when advanced features or deep hardware-level customizations are needed. Developers may find themselves restricted by the abstraction, missing access to device-specific capabilities that native APIs typically provide.
There’s also the risk of vendor lock-in. Many unified API platforms are built as part of a larger ecosystem. Once a product is tightly integrated with one provider’s stack, switching becomes costly and complex. Changes in pricing, platform support, or service quality can significantly impact future scalability and flexibility.
Customizing Integrations for Enhanced Customer Experiences
In today’s experience-driven tech landscape, integration doesn’t stop at enabling hardware and software to communicate, but it extends way beyond that. For businesses to succeed, adopting a customer-centric mindset that prioritizes customer experience (CX) is what truly makes the difference. Meaning, people don’t just go behind flashy features or efficient integrations anymore, what truly matters is how personalized and intuitive the experience feels.
Take Apple, for instance. They’ve built an entire ecosystem of custom integrations, blending state-of-the-art hardware, software, and services, ranging from the iPhone to the Apple Watch to the Vision Pro. What makes them unique is how each device is tightly integrated with the software, making them deeply aware of one another. This enables effortless handoff features, instant pairing, seamless data transfer, and context-aware automation, all with security embedded at the core.
The Advantages:
Businesses that invest in this level of personalization can often unlock greater operational efficiency, stronger customer engagement, and a genuine competitive edge. These integrations don’t just elevate product performance, they elevate them into experiences users genuinely want to come back to.
The Challenges:
Of course, going custom isn’t without its hurdles. Developing highly tailored systems requires time, cross-functional expertise, agile infrastructure, and a deep understanding of both user expectations and technical limitations. It also introduces complexity in terms of scaling, so what works brilliantly for one use case might not translate cleanly to another, meaning more maintenance and more iterations as the product evolves. There’s also the not-so-small issue of time-to-market because crafting seamless integrations from scratch inevitably takes longer, especially when rigorous testing and QA are involved.
Summing Up
In this blog, we’ve explored the top trends shaping the future of hardware-software integrations. We touched on real-time data integration, the growing importance of customer experience, how unified APIs simplify communication between systems, the growing popularity of low-code development, and the game-changing role of AI in managing complex integrations.
Along the way, we’ve also unpacked the challenges that come with each trend, giving you a realistic view of what it takes to implement these technologies effectively. Because successful integration isn’t just about connecting parts, it’s about designing systems that adapt and grow with your business and deliver value to your users every step of the way.
Because integrating advanced systems isn’t always plug-and-play, it demands foresight, adaptability, and a clear understanding of where technology meets user needs.
So whether you’re already exploring integration strategies or just starting to consider them, let this blog serve as your go-to guide when planning your next move. And if you’re unsure where to begin, our integration experts are here to help you navigate the path forward.